Changing States – Melting and Freezing
📚 Key Concepts
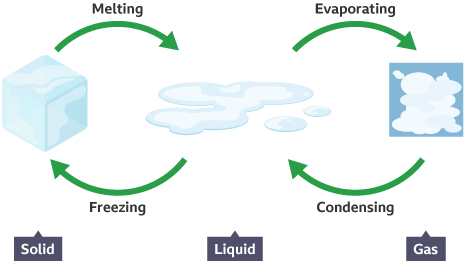
🔹 How Do States Change?
Heating Effects:
- Ice → Water: Melting (solid to liquid)
- Water → Vapour: Evaporation (liquid to gas)
Cooling Effects:
- Vapour → Water: Condensation (gas to liquid)
- Water → Ice: Freezing (liquid to solid)
🔹 State Change Processes
1. Melting
- Conversion of solid to liquid
- Requires heat energy
- Examples: Ice melting, candle wax melting, butter melting
2. Freezing
- Conversion of liquid to solid
- Releases heat energy
- Examples: Water freezing to ice, wax solidifying
3. Evaporation
- Conversion of liquid to gas
- Requires heat energy
- Happens at surface at all temperatures
4. Condensation
- Conversion of gas to liquid
- Releases heat energy
- Happens when gas is cooled
🔹 Other Substances That Change States
Examples:
- Candle wax: Solid → Liquid → Solid
- Coconut oil: Liquid in summer → Solid in winter
- Ghee: Solid when cool → Liquid when heated
- Chocolate: Solid → Liquid when heated
