What is Matter?
📚 Key Concepts
🔹 Definition of Matter
Matter is anything that occupies space (has volume) and has mass.
Fundamental Properties of Matter:
- Mass – quantity of matter
- Volume – space occupied by matter
Universal Definition:
- Everything around us is made of matter
- From tiny atoms to massive stars
- Includes solids, liquids, and gases
- Even invisible air is matter
🔹 Examples of Matter
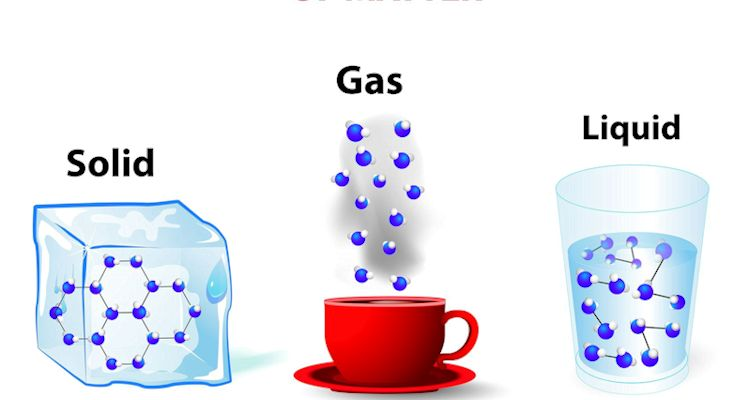
Solid Matter:
- Chair, table, book, stone, metal
- Have definite shape and volume
- Particles closely packed
- Strong intermolecular forces
Liquid Matter:
- Water, oil, milk, juice
- Have definite volume but no definite shape
- Take shape of container
- Moderate intermolecular forces
Gaseous Matter:
- Air, oxygen, carbon dioxide
- No definite shape or volume
- Fill entire container
- Weak intermolecular forces
🔹 Materials as Forms of Matter
Key Understanding:
- All materials are different forms of matter
- Materials are matter used to make objects
- Different arrangements of atoms/molecules create different materials
- Properties depend on composition and structure
Examples:
- Iron is matter used to make tools
- Wood is matter from trees used for furniture
- Plastic is matter created from petroleum
- Glass is matter made from sand and other materials
🔹 Matter vs. Non-Matter
What IS Matter:
- Air (has mass and volume)
- Light bulb (solid matter)
- Water vapor (gaseous matter)
- Smoke (mixture of gases and particles)
What is NOT Matter:
- Light (electromagnetic radiation)
- Heat (form of energy)
- Sound (pressure waves)
- Thoughts and emotions
🔹 States of Matter
Three Main States:
1. Solid State:
- Fixed shape and volume
- Particles vibrate in fixed positions
- Examples: Ice, wood, metal
2. Liquid State:
- Fixed volume but shape changes
- Particles move freely but stay together
- Examples: Water, oil, mercury
3. Gaseous State:
- No fixed shape or volume
- Particles move freely in all directions
- Examples: Air, water vapor, oxygen
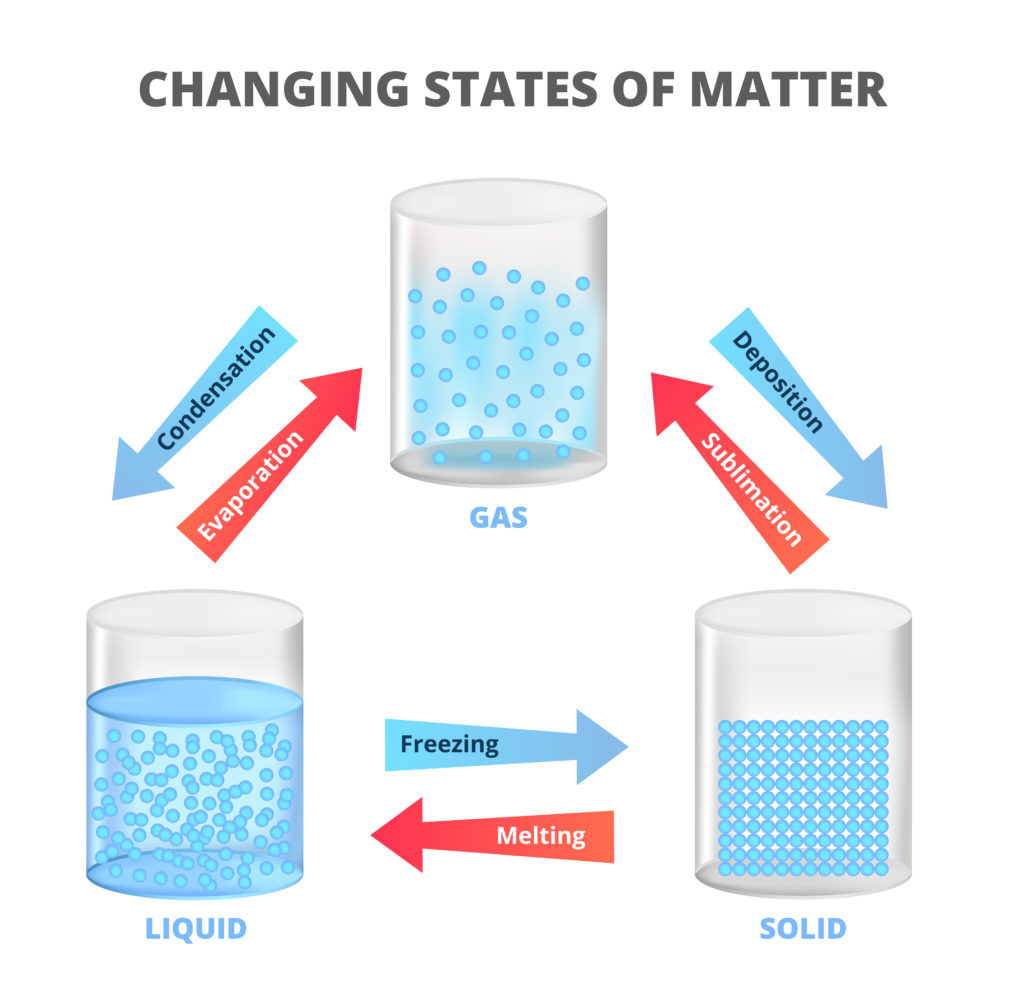
🔹 Conservation of Matter
Important Principle:
- Matter cannot be created or destroyed
- Can change from one form to another
- Total amount remains constant
- Basis for recycling and reuse
Examples:
- Water freezing to ice (liquid to solid)
- Ice melting to water (solid to liquid)
- Water evaporating to vapor (liquid to gas)
- Burning wood changes form but matter conserved
🔹 Matter in the Universe
Scale of Matter:
- Microscopic: Atoms, molecules
- Everyday: Objects around us
- Macroscopic: Planets, stars, galaxies
- Universal: All matter in cosmos
Composition:
- Made of atoms and molecules
- Different arrangements create different materials
- Chemical bonds hold atoms together
- Energy holds matter together
