Human Development
Introduction to Human Development
- Human Development means enlarging people’s choices & improving their quality of life.
- It goes beyond income & money → includes health, education, and living standards.
- Famous idea: Dr. Mahbub ul Haq introduced the concept.
- UNDP (United Nations Development Programme) publishes Human Development Report (HDR) every year.

Literacy Rate in India
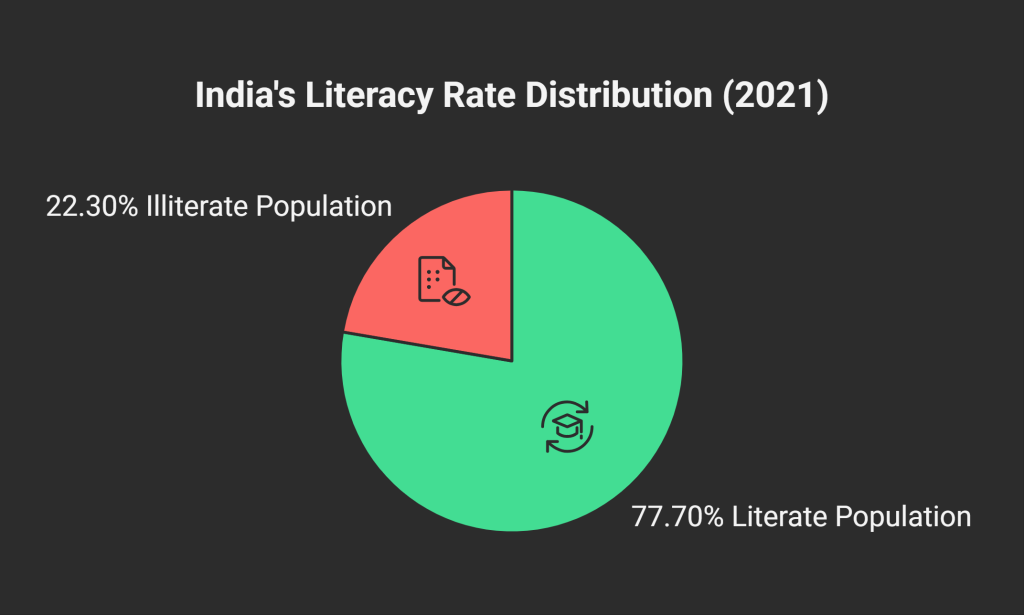
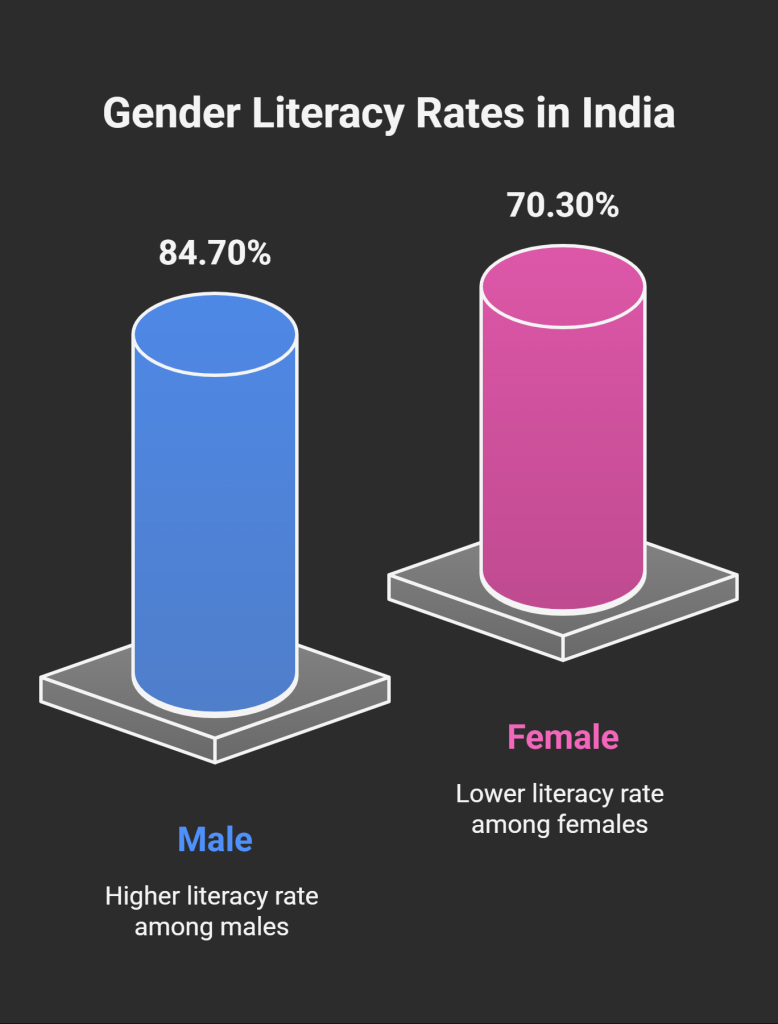
India’s average literacy rate (NSO 2021) → 77.70% (Male: 84.70%, Female: 70.30%)
Male literacy higher than female literacy → shows a gender gap in education.
Human Development Report (2020)
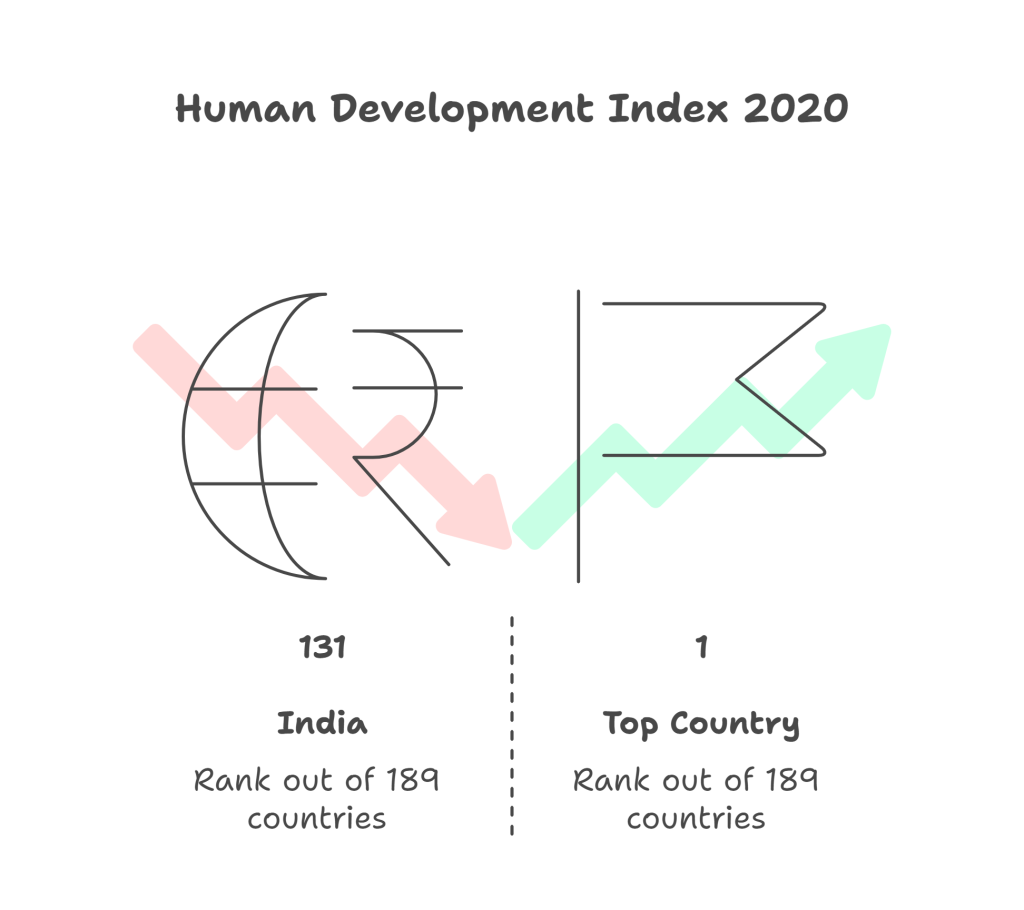
Out of 189 countries, India ranked 131 on the HDI 2020 (UNDP) with an HDI value of 0.645 — category: medium human development.
Report by UNDP → compares countries.
India ranked 131 out of 189 countries (2020).
HDI (Human Development Index) is based on 3 dimensions:
- Health → Life expectancy at birth
- Education → Mean years of schooling & expected years of schooling
- Standard of living → Gross National Income (GNI) per capita
👉 Exam tip: HDI ≠ just GDP!
Mortality Rate (NMR – Neonatal Mortality Rate)
India’s average neonatal mortality rate (NMR) — deaths in the first 28 days per 1,000 live births — fell from ~30 (2015–16) to 25 (2019–21).
- Neonatal Mortality Rate = Number of deaths of newborns (0–28 days) per 1,000 live births.
- Indicator of health facilities, nutrition & mother’s care.
- Lower NMR = better development.
- India has improved but still lags behind developed nations.

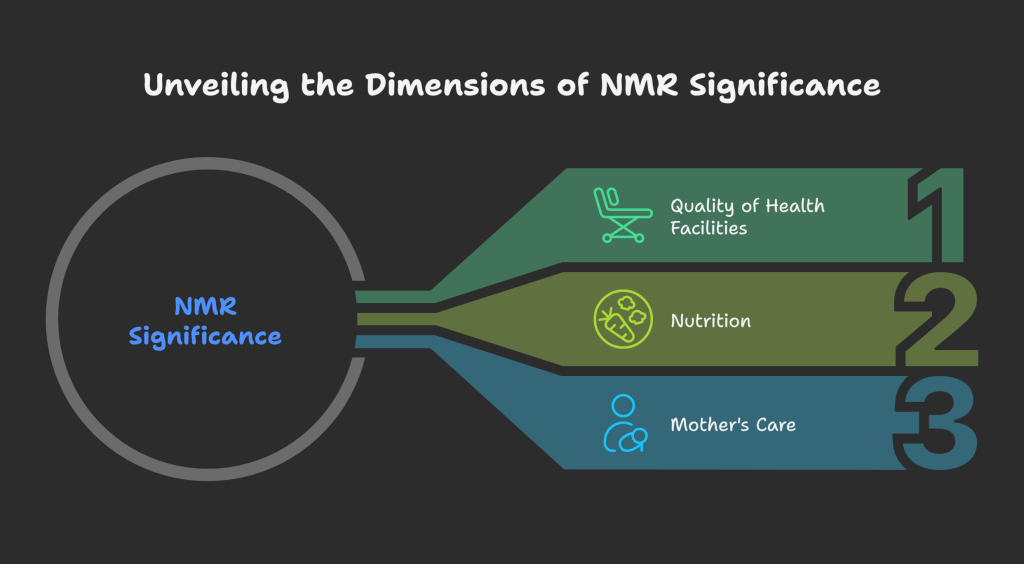
Significance of NMR
Health Facilities → Low NMR = good hospitals & emergency care.
Nutrition → Low NMR = better maternal & newborn nutrition.
Mother’s Care → Low NMR = proper prenatal & postnatal care.
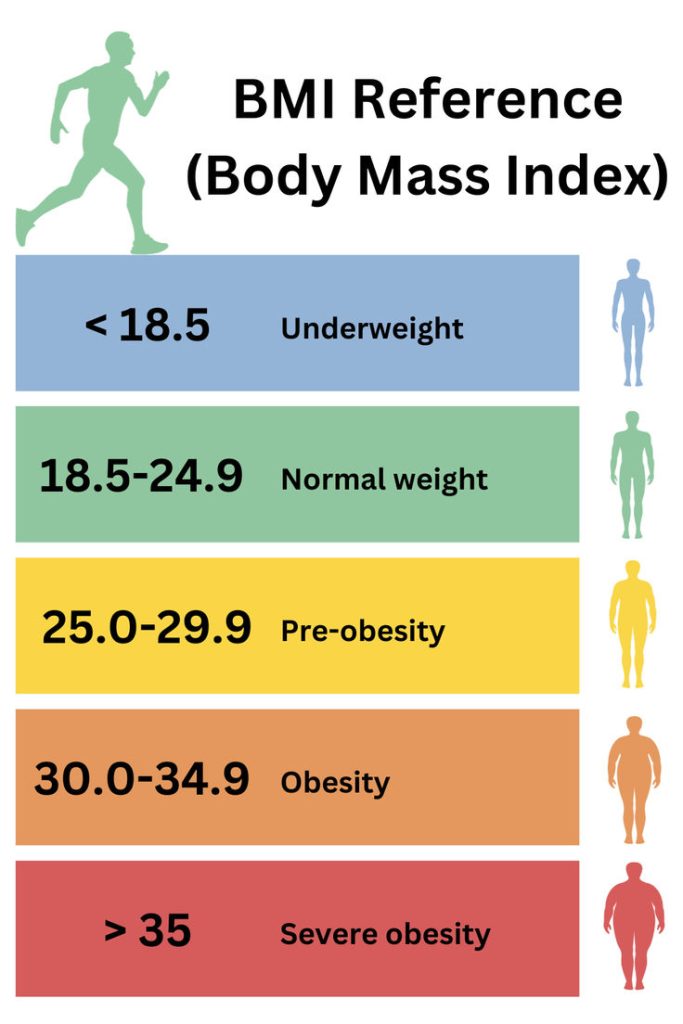
Body Mass Index (BMI)
BMI is calculated using height and weight.
BMI = Weight (kg) ÷ Height (m²).
Used to check nutritional health.
Categories:
- < 18.5 → Underweight
- 18.5 – 24.9 → Normal
- 25 – 29.9 → Overweight
- 30 & above → Obese
Human Development vs Economic Development
| Human Development | Economic Development |
|---|---|
| Broader: includes monetary + non-monetary aspects | Narrow: focuses on monetary aspect only |
| Includes quantitative + qualitative growth | Includes quantitative growth only |
| End/goal of all development | Means to achieve human development |
Components of Human Development
| Component | Meaning (as used in HDI) | Note/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Longevity | Life expectancy in years of a country’s people | Greater life expectancy → more developed. In India, life expectancy is stated as 65 years; in developed countries like Japan it is 70+ years. |
| Educational Attainment | Average education levels (adult literacy, combined enrolment: primary/secondary/tertiary) | Knowledge is measured via literacy and enrolment ratios. |
| Real Per Capita Income | Average income earned at a given time (price-adjusted) | Increase in real per capita income is treated as a key indicator of human development. |
India & Neighbours — Selected Data (2019)
| Country | GNI per Capita (2011 PPP $) | Life Expectancy at Birth (yrs) | Mean Years of Schooling (25+) | HDI Rank (2018) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sri Lanka | 12,707 | 77 | 10.6 | 73 |
| India | 6,681 | 69.7 | 6.5 | 130 |
| Myanmar | 4,961 | 67.1 | 5.0 | 148 |
| Pakistan | 5,005 | 67.3 | 5.2 | 154 |
| Nepal | 3,457 | 70.8 | 5.0 | 143 |
| Bangladesh | 4,976 | 72.6 | 6.2 | 134 |
Notes:
- HDI = Human Development Index; ranks out of 189 countries.
- Life expectancy at birth = average expected length of life at birth.
- Per capita income shown in dollars to compare; adjusted so each dollar buys the same basket across countries.
Sustainable Development
Definition: Economic development that maintains quality of life for both present and future generations without harming natural resources and the environment.
Examples: Groundwater in India; Exhaustion of natural resources.
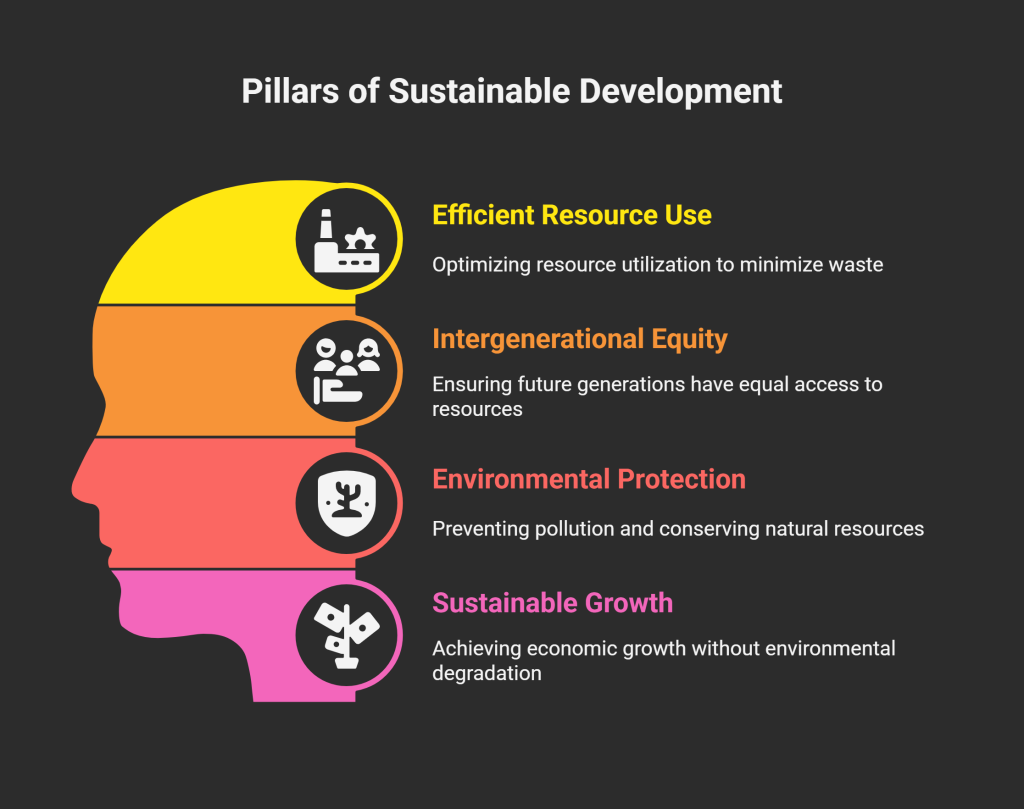
Features of Sustainable Development
- Efficient use of natural resources to raise income/employment, reduce poverty, improve living standards.
- No reduction in quality of life for future generations.
- No increase in pollution; protect environmental quality for the future.
- Does not limit development: use resources so present and future growth can be maintained.

Steps Towards Sustainable Development
- Increased use of renewable & clean energy sources
- Less use of fossil fuels
- Organic farming
- Measures to reduce global warming and global limits on carbon emissions
Conclusion
“We have not inherited this earth from our forefathers; we have borrowed it from our children.”
“Earth has enough resources to meet the needs of all, but not the greed of even one person.”
