Levels of Organization in Living Organisms
📚 Key Concepts
🔹 Organizational Hierarchy
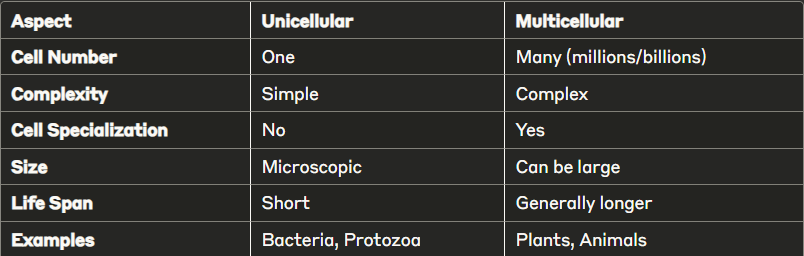
The Five Levels of Organization:
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ System → Organism
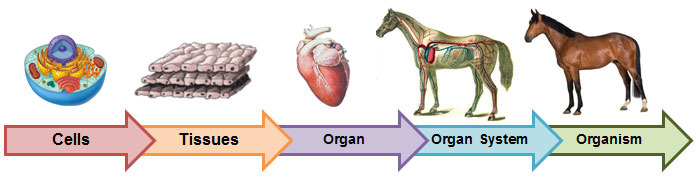
1. Cell
- Basic building block of life
- Like bricks in a wall
- Can function independently (in unicellular organisms)
2. Tissue
- Group of similar cells working together
- Examples: Muscle tissue, nerve tissue
- Specialized for specific functions
3. Organ
- Collection of different tissues
- Examples: Heart, liver, leaf, root
- Performs complex functions
4. Organ System
- Multiple organs working together
- Examples: Digestive system, respiratory system
- Carries out major body functions
5. Organism
- Complete living being
- All organ systems working together
- Examples: Human, plant, animal
🔹 Unicellular vs Multicellular Organisms
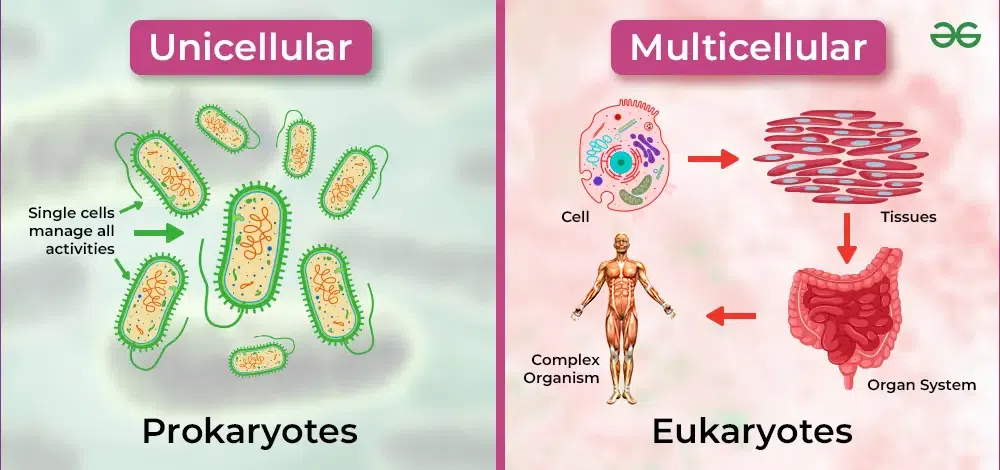
Unicellular Organisms:
- Made of single cell
- All life processes occur in one cell
- Examples: Bacteria, Amoeba, Paramecium
- Simple structure, basic functions
Multicellular Organisms:
- Made of many cells
- Cells have specialized functions
- Examples: Humans, plants, animals
- Complex structure, advanced functions
Key Differences: