Beneficial Microorganisms
📚 Key Concepts
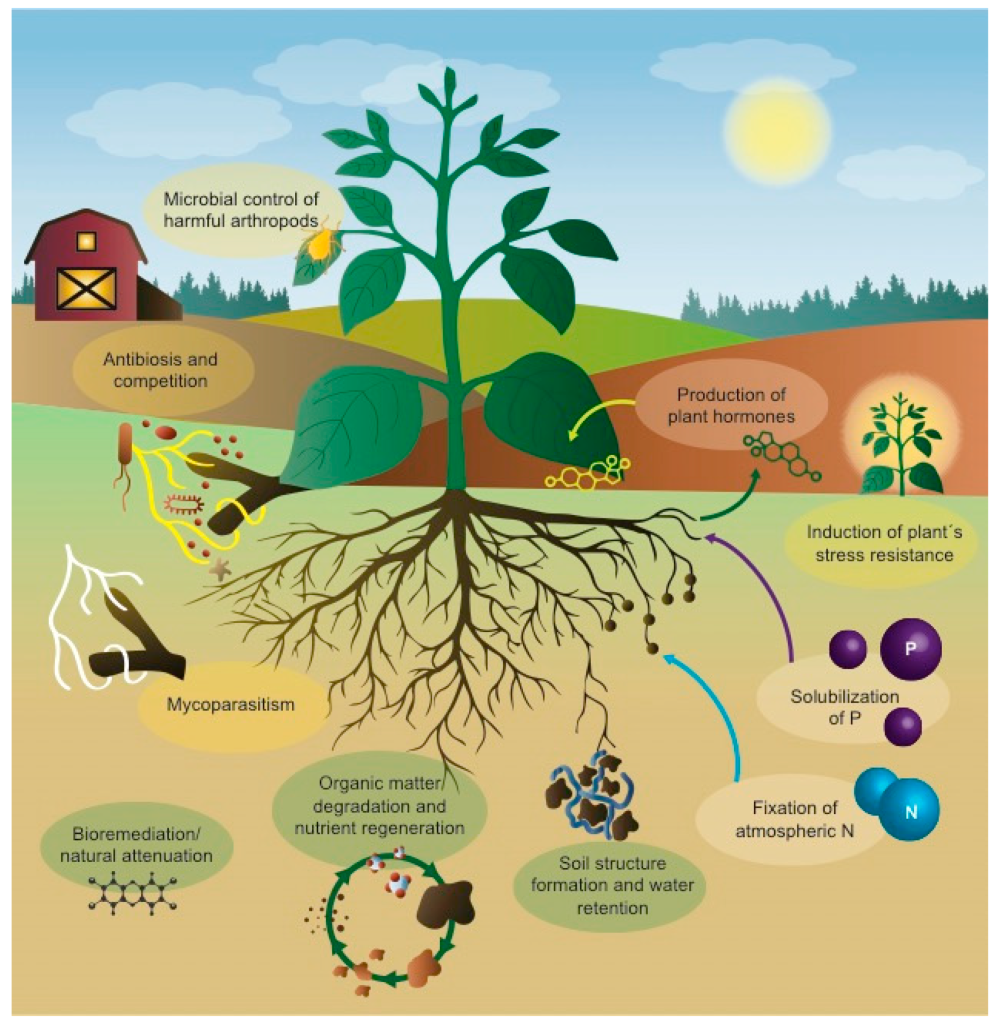
🔹 Environmental Cleaners – Decomposers
Role of Decomposer Microorganisms:
Primary Decomposers:
- Bacteria: Break down proteins and complex molecules
- Fungi: Decompose cellulose and lignin in plants
Decomposition Process:
- Organic Matter: Dead plants and animals
- Microbial Action: Enzymes break down complex compounds
- Simple Compounds: Released back to environment
- Nutrient Cycling: Elements return to soil and atmosphere
Benefits:
- Waste Management: Natural recycling system
- Soil Fertility: Nutrients returned to soil
- Environmental Cleanup: Prevents accumulation of dead matter
- Carbon Cycle: CO₂ returned to atmosphere
Real-life Applications:
- Composting: Kitchen waste to manure
- Sewage Treatment: Bacterial breakdown of waste
- Bioremediation: Cleaning oil spills and pollution
- Landfill Management: Waste decomposition
🔹 Nitrogen Fixation – Soil Enrichers
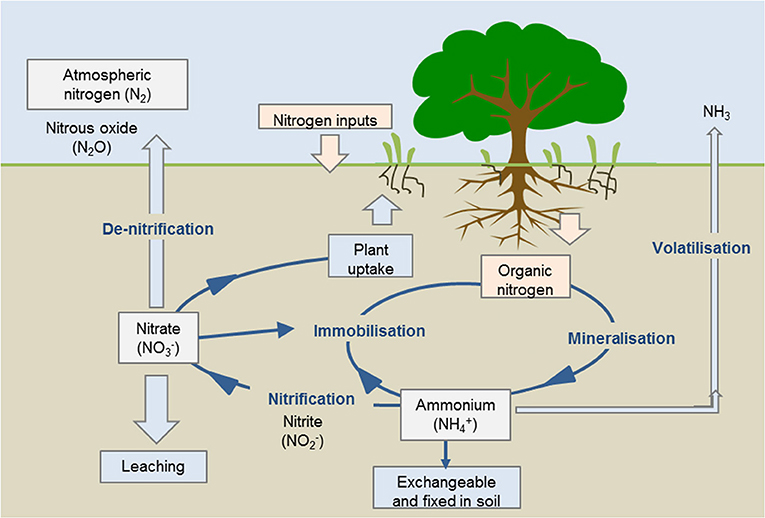
Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria:
Rhizobium Bacteria:
- Location: Root nodules of legume plants
- Function: Convert atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) to ammonia (NH₃)
- Benefit: Plants get nitrogen without fertilizers
- Examples: In roots of peas, beans, lentils, soybeans
Process:
- Atmospheric Nitrogen: Abundant but unusable by plants
- Bacterial Conversion: N₂ → NH₃ (ammonia)
- Plant Uptake: Ammonia used for protein synthesis
- Soil Enrichment: Nitrogen compounds released
Agricultural Benefits:
- Reduced Fertilizer Use: Natural nitrogen supply
- Crop Rotation: Legumes improve soil for next crop
- Sustainable Farming: Environmentally friendly
- Cost Reduction: Lower input costs for farmers
🔹 Food Production and Processing

Microorganisms in Food Industry:
1. Bread and Baking Industry
- Organism: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Baker’s yeast)
- Process: Fermentation of sugars
- Products: CO₂ (makes dough rise) + Ethanol (evaporates)
- Applications: Bread, cakes, pastries, pizza dough
Fermentation Reaction: C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2C₂H₅OH + 2CO₂ (Glucose → Ethanol + Carbon dioxide)
2. Dairy Industry
- Organism: Lactobacillus bacteria
- Process: Lactic acid fermentation
- Products: Lactic acid (gives sour taste)
- Applications: Yogurt, cheese, buttermilk, sour cream
Lactic Acid Fermentation: C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2C₃H₆O₃ (Glucose → Lactic acid)
3. Traditional Fermented Foods
- Idli/Dosa: Fermented rice and lentil batter
- Dhokla: Fermented chickpea batter
- Kimchi: Fermented cabbage
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage
- Pickles: Preserved using fermentation
4. Alcoholic Beverages
- Beer: Fermented grains (barley, wheat)
- Wine: Fermented grapes
- Traditional drinks: Rice wine, palm wine
🔹 Medicine and Biotechnology

Therapeutic Applications:
1. Antibiotic Production
- Penicillin: From Penicillium fungi
- Streptomycin: From Streptomyces bacteria
- Tetracycline: From Streptomyces species
2. Vaccine Production
- Bacterial vaccines: Using weakened bacteria
- Viral vaccines: Using modified viruses
- Recombinant vaccines: Using genetically modified microbes
3. Probiotic Therapy
- Good bacteria: Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium
- Benefits: Improve digestive health
- Applications: Treating digestive disorders
4. Industrial Applications
- Enzyme Production: Industrial enzymes from microbes
- Biofuel: Ethanol and methane from microbial fermentation
- Pharmaceuticals: Various medicines from microorganisms
