Threats to Life on Earth
📚 Key Concepts
🔹 The Triple Planetary Crisis
Modern human activities threaten Earth’s delicate balance through three major challenges:

1. Climate Change
Causes:
- Burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, gas)
- Deforestation reducing CO₂ absorption
- Industrial processes releasing greenhouse gases
- Agriculture producing methane
Greenhouse Gases:
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂): 76% of emissions
- Methane (CH₄): 16% of emissions
- Nitrous oxide (N₂O): 6% of emissions
- Fluorinated gases: 2% of emissions
Effects:
- Global temperature rise (already +1.1°C since 1880)
- Melting ice caps and glaciers
- Rising sea levels
- Extreme weather events
- Shifts in precipitation patterns
- Ecosystem disruption
2. Biodiversity Loss
Causes:
- Habitat destruction for agriculture and cities
- Pollution contaminating ecosystems
- Overfishing and hunting
- Climate change altering habitats
- Invasive species disrupting ecosystems
Consequences:
- Species extinction (1,000-10,000 times natural rate)
- Ecosystem collapse
- Loss of pollination services
- Reduced food security
- Loss of potential medicines
3. Pollution
Air Pollution:
- Particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10)
- Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ)
- Sulfur dioxide (SO₂)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Ozone at ground level
Water Pollution:
- Industrial chemicals and heavy metals
- Agricultural runoff (fertilizers, pesticides)
- Plastic waste and microplastics
- Sewage and untreated wastewater
- Oil spills
Soil Pollution:
- Chemical contamination
- Excessive fertilizer use
- Pesticide accumulation
- Industrial waste disposal
- Plastic contamination
🔹 Impact on Earth’s Systems
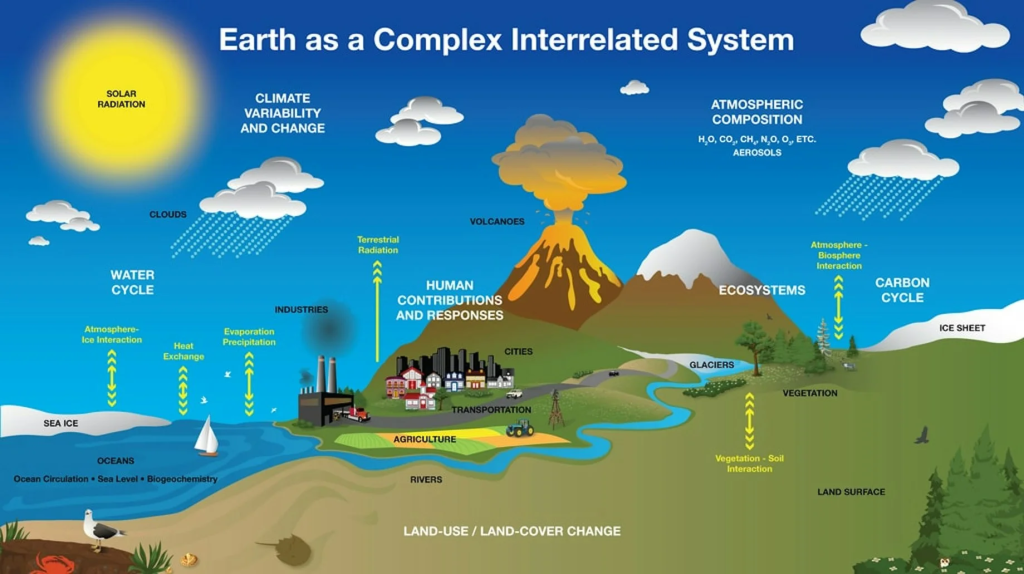
Atmosphere Changes:
- Increased greenhouse gas concentrations
- Ozone layer depletion (recovering due to Montreal Protocol)
- Air quality degradation
- Acid rain formation
Hydrosphere Changes:
- Ocean acidification from CO₂ absorption
- Water temperature rise
- Pollution of freshwater sources
- Microplastic contamination
Geosphere Changes:
- Soil degradation and erosion
- Mineral resource depletion
- Landscape modification
- Waste accumulation
Biosphere Changes:
- Species extinction and endangerment
- Ecosystem fragmentation
- Food web disruption
- Reduced genetic diversity
